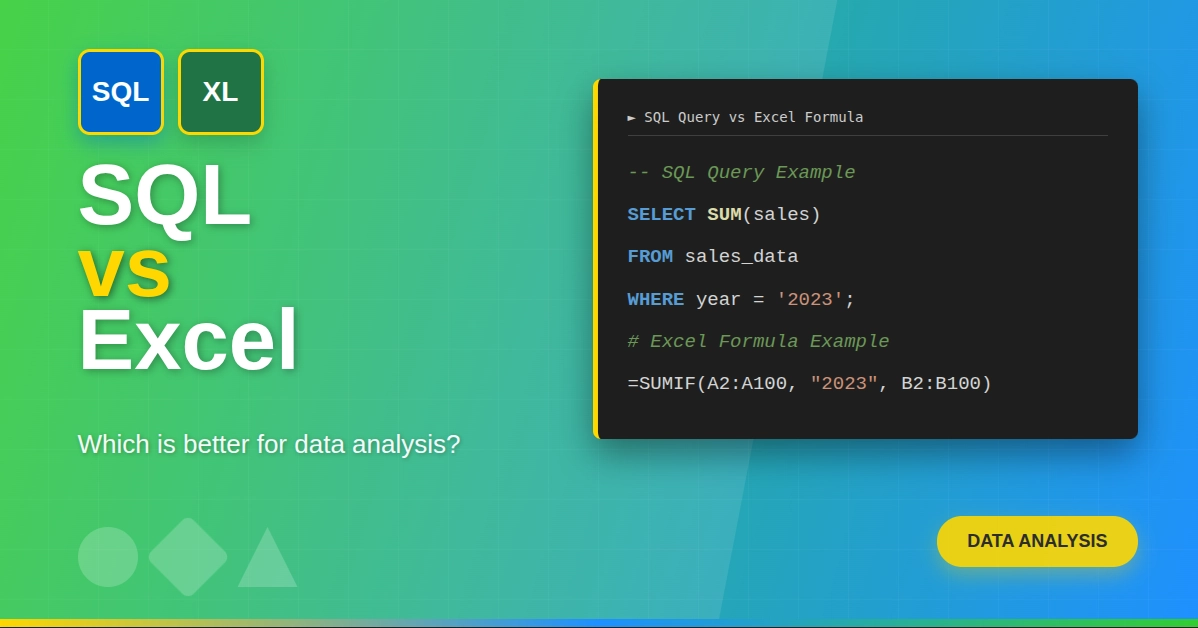
SQL, which stands for “Structured Query Language,” is the primary language for managing and manipulating relational databases. We use SQL commands to tell the database what actions we want it to perform.
SQL commands are instructions used to interact with a relational database management system (RDBMS) to perform various operations, including retrieving, manipulating, and managing data and the database structure. They give you control over how your data is organized and stored. For example, you can use a command to pull a list of all customers in New York.
This guide covers the five main types of SQL commands – DDL, DML, DQL, DCL, and TCL – with syntax tables and code examples for every single command.
Master SQL and Database management with this SQL course: Practical training with guided projects, AI support, and expert instructors.
SQL Commands Cheat Sheet
A quick reference for the most common commands.
| Command | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ALTER | DDL | Adds or modifies columns in a table. |
| COMMIT | TCL | Saves changes permanently. |
| CREATE | DDL | Creates a new table or database. |
| DELETE | DML | Removes rows from a table. |
| DROP | DDL | Deletes a table entirely. |
| GRANT | DCL | Gives a user access permissions. |
| INSERT | DML | Adds new rows to a table. |
| JOIN | DQL | Combines data from two tables. |
| ROLLBACK | TCL | Undoes recent changes. |
| SELECT | DQL | Retrieves data. |
| TRUNCATE | DDL | Wipes all data but keeps the table. |
| UPDATE | DML | Edits existing data. |
Master SQL and Database management with this SQL course: Practical training with guided projects, AI support, and expert instructors.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands define the structure (schema) of your database. They help you create, modify, or delete the containers (tables, databases) that store your data, without affecting the data itself.

1. CREATE:
Creates a new database or table.
Example:
CREATE TABLE Employees (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(100),
Age INT,
Department VARCHAR(50)
);
2. ALTER:
Modifies the structure of an existing table (e.g., adding, deleting, or modifying columns).
Example:
ALTER TABLE Employees
ADD Salary DECIMAL(10, 2);
3. DROP:
Deletes a table and all its data permanently.
Example:
DROP TABLE Employees;
4. TRUNCATE:
Deletes all data inside a table but keeps the structure.
Example:
TRUNCATE TABLE Employees;
5. RENAME:
Changes the name of a database object (like a table or column).
Example:
RENAME TABLE Employees TO Staff;
6. COMMENT:
Adds or modifies a comment on a database object (like a table or column).
Example:
COMMENT ON COLUMN Employees.Name IS 'Employee Name';
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands manage the data within your database. They allow you to add, edit, or remove records in the tables, working with the data inside the structure created by DDL.

7. INSERT:
Adds new records to a table.
Example:
INSERT INTO Employees (ID, Name, Age, Department)
VALUES (1, 'John Doe', 30, 'HR');
8. UPDATE:
Modifies existing records in a table.
Example:
UPDATE Employees
SET Age = 31
WHERE ID = 1;
9. DELETE:
Removes records from a table.
Example:
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE ID = 1;
Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL commands manage security, access, and permissions. They control who can view or edit data, ensuring only authorized users can modify sensitive information.

10. GRANT:
This command gives permissions to users or roles. You can grant permissions such as SELECT (view), INSERT (add data), UPDATE (modify data), and DELETE (remove data).
Example:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON Employees TO user123;
11. REVOKE:
This command removes permissions from users or roles. It takes away rights that were previously granted. You can revoke permissions like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
Example:
REVOKE SELECT, INSERT ON Employees FROM user123;
12. DENY:
This command denies permissions to users or roles. Even if a user has been granted certain permissions, this command blocks specific actions. You can deny permissions like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
Example:
DENY DELETE ON Employees TO user123;
Data Query Language (DQL)
DQL commands are used to retrieve data from the database. It focuses only on reading information, not changing it.
The primary DQL command is SELECT. It can be combined with clauses like WHERE, JOIN, and HAVING to refine results and analyze data in detail.
13. SELECT:
The SELECT command retrieves data from a database using clauses such as WHERE, JOIN, and HAVING to refine and filter the results.
Example:
SELECT Name, Age FROM Employees WHERE Department = 'Sales';
Use of SELECT with different clauses:
-- SELECT + WHERE
SELECT Name, Age FROM Employees WHERE Department = 'Sales';
-- SELECT + WHERE + ORDER BY
SELECT Name, Salary FROM Employees WHERE Salary > 50000 ORDER BY Salary DESC;
-- SELECT + JOIN
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.Name AS DeptName FROM Employees JOIN Departments ON Employees.DeptID = Departments.ID;
-- SELECT + GROUP BY + HAVING
SELECT Department, COUNT(*) AS TotalEmployees FROM Employees GROUP BY Department HAVING COUNT(*) > 10;
-- SELECT + DISTINCT
SELECT DISTINCT Department FROM Employees;
-- SELECT + ORDER BY + LIMIT
SELECT Name, Age FROM Employees ORDER BY Age DESC LIMIT 5;
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL is a set of SQL commands used to manage transactions. A transaction is a group of SQL operations that should be treated as a single unit. TCL ensures that either all actions in a transaction are saved, or none are saved if something goes wrong.

The TCL commands are:
14. COMMIT
The COMMIT command saves all changes made during the current transaction to the database.
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE employees SET salary = 5000 WHERE id = 1;
COMMIT;
In this example, the salary update is saved to the database.
15. ROLLBACK
The ROLLBACK command undoes all mistaken changes made during the current transaction.
Example:
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE employees SET salary = 5000 WHERE id = 1;
ROLLBACK;
Here, the salary update is undone, and the data remains unchanged.
16. SAVEPOINT
The SAVEPOINT command sets a point within a transaction that you can roll back to if needed.
Example:
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE employees SET salary = 5000 WHERE id = 1;
SAVEPOINT salary_update;
UPDATE employees SET salary = 6000 WHERE id = 2;
ROLLBACK TO salary_update;
COMMIT;
In this example, if the second update causes an issue, you can roll back to the salary_update point, keeping the first update intact.
17. SET TRANSACTION
The SET TRANSACTION command is used to set properties for the current transaction, such as isolation level.
Example:
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL SERIALIZABLE;
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE employees SET salary = 5000 WHERE id = 1;
COMMIT;
This sets the isolation level to SERIALIZABLE, ensuring that no other transactions can access the data until the current transaction completes.
Other SQL Resources: