In 2026, the role of a Prompt Engineer has fundamentally changed. It is no longer about just writing clever sentences to a chatbot.
The industry now defines this role as an AI Systems Engineer or LLM Ops Specialist.
A Prompt Engineer is responsible for designing, optimizing, and evaluating the interaction layer between human intent and Large Language Models (LLMs).
This is a technical discipline. It requires building systematic evaluations (known as "evals"), architecting retrieval pipelines (RAG), and implementing programmatic prompting frameworks.
The primary objective is to maximize model performance, specifically accuracy, latency, and cost, without ever altering the model’s internal weights.
Prompt Engineering vs. AI Development
Understanding the distinction between a Prompt Engineer and an AI Developer is critical for career positioning.
While both roles interact with Artificial Intelligence, their technical focus is completely different.
The Core Distinction
There is one fundamental difference that separates these two paths:
- An AI Developer treats the LLM as a trainable artifact. They modify the internal parameters (weights) using backpropagation and gradient descent.
- A Prompt Engineer treats the LLM as a frozen inference engine. They program the model via context, retrieval schemas, and instruction sets.
Here is the detailed technical comparison:
| Feature | Prompt Engineer (AI Systems/Product) | AI Developer (Core Model/ML Engineer) |
| Primary Goal | Optimize model behavior and output quality for specific use cases. | Optimize model architecture, training, and infrastructure. |
| Key Input | Context windows, instruction sets, few-shot examples, retrieval schemas. | Large datasets, neural network weights, loss functions, hyperparameters. |
| Core Tools | DSPy, LangSmith, LangFuse, PromptLayer, OpenAI Playground, Anthropic Console. | PyTorch, TensorFlow, CUDA, Hugging Face Transformers, AWS Sagemaker. |
| Iteration Cycle | Minutes to Hours (Modify prompt -> Run Eval -> Deploy). | Days to Weeks (Data prep -> Train -> Validate -> Deploy). |
| Technical Depth | In-Context Learning (ICL): Designing context to mimic training. Focus on token economics and retrieval logic. | Gradient Descent: Modifying floating-point weights via backpropagation. Focus on mathematical convergence. |
| Code Focus | Python/TypeScript for orchestration, evaluation logic, and API integration. | Python/C++ for model training loops and inference optimization. |
The Bottom Line: A Prompt Engineer works "above" the model API, optimizing the input and output. An AI Developer works "below" the API, optimizing the neural network itself.
Professional Responsibilities (The Daily Workflow)
The day-to-day workflow of a Prompt Engineer follows a Test-Driven Development (TDD) approach.
It is not a creative writing process. It is a circular, metric-based engineering cycle.
The workflow consists of three distinct phases.
Phase 1: Context Architecture & Strategy
This phase focuses on constructing the input data to ensure the model has the correct information to process. It involves three specific tasks:
1. System Prompt Design
This is the foundational instruction set. The engineer constructs complex "system messages" that define the persona, operational constraints, and the output schema. This often involves enforcing strict formats, such as JSON or YAML, to ensure the output can be parsed by software.
2. Context Engineering
Context windows are limited and expensive. The engineer must manage this resource effectively. This involves "Passage Ranking" - selecting which data to include, and formatting that data (using XML tags or Markdown) to minimize hallucination.
3. Decomposition
Complex user queries often cause models to fail. The engineer breaks these queries into sequential steps. Techniques used here include:
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT): Instructing the model to outline its reasoning before giving an answer.
- Least-to-Most Prompting: Solving simple sub-problems before tackling the main query.
Phase 2: Systematic Evaluation (The "Evals")
This is the most critical differentiator between a hobbyist and a professional.
You cannot improve what you cannot measure. Therefore, the Prompt Engineer spends 40-50% of their time building evaluations.
1. Dataset Creation
The engineer builds "Gold Sets." These are datasets containing inputs and their corresponding ideal outputs (ground truth). These sets are used to benchmark the model's performance.
2. Metric Definition
The engineer implements programmatic metrics using frameworks like RAGAS or DeepEval. Common metrics include:
- Faithfulness: Does the answer come strictly from the retrieved context, or did the model invent information?
- Answer Relevance: Does the answer directly address the user's query?
- Context Precision: What is the signal-to-noise ratio in the documents provided to the model?
3. LLM-as-a-Judge
It is impossible to manually grade thousands of outputs. The engineer configures stronger models (like GPT-4o or Claude 3.5 Sonnet) to grade the outputs of smaller, faster models based on the defined criteria.
Phase 3: Optimization & Deployment
Once a baseline is established via evals, the system is optimized for production.
1. Hyperparameter Tuning
The engineer adjusts settings to control output diversity:
- Temperature: Controls randomness.
- Top_p: Controls nucleus sampling (limiting the token pool).
- Frequency Penalty: Discourages repetition.
Suggested Read: Hypermeter Tuning Explained
2. Programmatic Optimization
Using frameworks like DSPy, the engineer automatically compiles and optimizes prompts based on validation data. This replaces manual trial-and-error with mathematical optimization.
3. Cost Management
A major responsibility is reducing API costs. A common strategy is Model Routing: sending complex queries to expensive "Reasoning" models and simple queries to cheap "Flash" or "Mini" models.
Skills Required for Prompt Engineers
To secure a high-paying role, "good English" is not enough. Specific technical competencies are required.
A. Core Technical Skills
- Python Proficiency
Python is the language of AI orchestration. A Prompt Engineer must read and write Python to interact with APIs (OpenAI, Anthropic, Vertex AI) and build evaluation loops.
Key Libraries: requests, pandas, pydantic.
- Programmatic Prompting (DSPy)
Manual string manipulation is obsolete. Knowledge of DSPy is the industry standard. This framework abstracts prompts into "modules" and "optimizers," treating prompts like machine learning parameters that can be tuned automatically.
- RAG Architecture
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is mandatory. The engineer must understand:
- Chunking: Splitting text into fixed-size or semantic segments.
- Vector Embeddings: Converting text into numerical representations for cosine similarity search.
- Retrieval Debugging: Identifying when the correct document is retrieved, but the model ignores it.
B. Specialized Engineering Concepts
- Structured Outputs
Enterprise applications require structured data. The engineer must know how to force models to output valid JSON or Pydantic objects using tools like Instructor or Outlines.
- Agentic Workflows
This involves building systems where the LLM can use external tools (web search, calculators, APIs). The engineer must understand ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) patterns and how to define tool definitions (function calling).
- Version Control for Prompts
Prompts are code. They must be tracked. The engineer uses platforms like LangSmith or PromptLayer to track changes in prompts over time, identical to how Git tracks code.
C. Analytical Skills
The engineer analyzes evaluation logs to detect patterns. For example: "The model consistently fails on negation" or "The model exhibits bias towards the first document provided."
- A/B Testing
The engineer designs experiments to statistically prove that Prompt Version B is superior to Prompt Version A before deployment.
How to Become a Prompt Engineer (The Roadmap)
Most advice on becoming a Prompt Engineer is incorrect. It focuses on writing text. Now, the market requires engineers who can control non-deterministic systems using code.
Here is the technical roadmap to transition from a general user to an AI Prompt Engineer.
Step 1: Understand the Stochastic Nature of LLMs
Before writing code, you must understand how the model functions.
An LLM is a probability distribution engine. It predicts the next token based on the previous sequence of tokens. It does not "know" facts; it calculates the statistical likelihood of text sequences.
The Action Plan:
- Analyze Tokenization: Use the OpenAI Tokenizer tool. Observe how text is converted into integers. This explains why models often fail at character-level tasks (like reversing a word) or complex arithmetic.
- Control the Parameters: Learn the specific settings that control output variance.
- Temperature: Controls the flatness of the probability distribution (randomness).
- Top_P (Nucleus Sampling): Restricts the token selection to the top percentile of probabilities.
- Study In-Context Learning: Read the "Architecture" section of the GPT-3 paper (Brown et al.). Understand that "Few-Shot Learning" conditions the model's inference state without changing its permanent weights.
Step 2: Learn Python for API Integration
You do not need full-stack development skills (HTML/CSS). However, you must learn Python to interact with model APIs and process data. This is the primary language for AI orchestration.
The Syllabus:
- API Interaction: Master the
requestslibrary. Learn to send HTTP POST requests to OpenAI or Anthropic endpoints, handle authentication headers, and manage rate limits (429 errors). - Data Validation: Master
Pydantic. This library is essential for "Structured Outputs." You will use Pydantic to define exact classes (e.g., a specific JSON schema) that the LLM must generate for software integration. - Data Processing: Learn
Pandas. You will need to load and manipulate large datasets (CSV or Parquet files) to run bulk evaluations.
Step 3: Transition to Programmatic Prompting (DSPy)
This step marks the transition from manual drafting to engineering.
Manual prompting involves editing text strings in a file. Programmatic prompting involves defining logic that compiles into text.
The Tool: Adopt DSPy (Declarative Self-Improving Language Programs).
The Function: DSPy abstracts prompts into "Modules" (logic) and "Optimizers" (tuning). You define the pipeline (e.g., Retrieve $\to$ Reason $\to$ Answer), and the optimizer automatically selects the best few-shot examples and instructions based on performance data.
Step 4: Build a "Ground Truth" Evaluation Pipeline
Engineering requires measurement. You must prove reliability with data.
The Execution:
- Create a Ground Truth Dataset: Manually create a dataset of 50+ inputs and their correct, verified outputs.
- Implement "LLM-as-a-Judge": Write a Python script where a high-capability model (like GPT-4o) evaluates the outputs of your system against the ground truth.
- Track Metrics: Report specific performance indicators.
- Faithfulness: The percentage of outputs strictly derived from the retrieved context.
- Recall: The percentage of relevant information retrieved from the database.
Step 5: Execute an End-to-End Portfolio Project
Do not present chat logs as a portfolio. Build a functional system that solves a business problem.
Project Specification: The Automated RFP Responder
- Ingest: Write a script to load technical documentation (PDFs).
- Chunk & Embed: Split the text into semantic segments and store them in a Vector Database (e.g., Pinecone or ChromaDB).
- Retrieve: Configure the system to retrieve the top 3 relevant segments when a user asks a question.
- Synthesize: Use an LLM to generate an answer based strictly on the retrieved segments.
- Evaluate: Run your evaluation pipeline to test the accuracy of the answers.
Final Deliverable:
Host the code on GitHub. The README.md file must document the evaluation metrics and the improvement in accuracy achieved during the optimization phase.
Chapter 5: Job Market Data & Salary
The market places a premium on "Full-Stack Prompt Engineers", those who can code. Purely non-technical prompt roles are declining in value.
Salary Ranges (Annual)
| Region | Entry-Level (0-2 Years) | Mid-Level (2-4 Years) | Senior / Staff (5+ Years) |
| United States | $90,000 - $130,000 | $140,000 - $190,000 | $200,000 - $320,000 |
| Europe (Tier 1) | €50,000 - €75,000 | €80,000 - €110,000 | €120,000 - €160,000 |
| India | ₹8 - 15 Lakhs | ₹18 - 30 Lakhs | ₹40 - 70 Lakhs+ |
Job Titles to Search
When searching for roles, look for these titles:
- Prompt Engineer
- AI Systems Engineer
- LLM Evaluation Engineer
- Generative AI Product Engineer
- AI Implementation Specialist
Industry Demand
Certain sectors have a higher demand for these skills:
- Legal Tech: For contract analysis and discovery.
- Health Tech: For clinical note summarization and patient triage.
- Fintech: For fraud detection and regulatory compliance.
- Enterprise SaaS: For customer support automation and internal knowledge search.
Learning Resources (The Expert Stack)
Avoid generic "ChatGPT Masterclass" videos. They do not teach engineering.
Focus on resources used by engineering teams.
Documentation & Frameworks (Primary Sources)
- Anthropic's Prompt Engineering Guide: Widely considered the gold standard for technical prompting documentation.
- OpenAI Cookbook: A GitHub repository containing code snippets for clustering, embedding, and evaluations.
- DSPy Documentation: The official docs for the DSPy framework (Stanford NLP). This represents the future of programmatic prompting.
- LangChain / LangSmith Docs: Essential for understanding the tooling ecosystem.
Recommended Courses (Technical Focus)
Certificate Program in Applied Generative AI
Master the tools and techniques behind generative AI with expert-led, project-based training from Johns Hopkins University.
Free Prompt Engineering Course with Certificate
Learn prompt engineering for ChatGPT and improve accuracy with clear, effective prompts. Explore Generative AI, LLMs, and practical skills for content, coding, and real tasks.
Final Technical Advice
To succeed in this field, one must stop viewing the LLM as a person.
Start viewing it as a stochastic function:
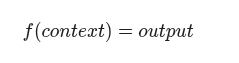
The job of a Prompt Engineer is to engineer the context to minimize the variance in the output.
Start by learning Python and Evals immediately. These are the barriers to entry for the high-paying roles.