While AI agents are widely discussed, only a limited number of organizations have successfully implemented them at scale.
This is often due to the challenges of integrating autonomous systems into existing human workflows, which can lead to operational friction, security risks, and process ambiguity.
Effective adoption requires more than technology investment; it requires a well-defined strategy.
Whether the goal is to automate customer support or streamline HR onboarding, this article outlines a structured, step-by-step approach to adopting AI agents for workflow automation, helping organizations reduce risk while maximizing return on investment.
Benefits of Implementing AI Agents
1. The Productivity Multiplier
- AI Agents move beyond simple efficiency; they create capacity. For example, instead of saving 5 minutes on a single email, an agent can manage the entire inbox context, draft responses based on past history, and schedule meetings autonomously.
- The Impact: Employees reclaim hours, not minutes, per week. This allows teams to shift focus from "keeping the lights on" to high-leverage work like strategy, creativity, and relationship building.
2. 24/7 Operational Continuity
- Unlike human employees, AI agents do not sleep, take vacations, or suffer from burnout. They provide "always-on" capabilities for critical, time-sensitive functions.
- The Impact: Customer service queries are resolved instantly at 2 AM, and IT system logs are monitored continuously. Your business keeps moving forward even when your team is offline.
3. Reduced Context Switching
- Frequent switching between applications, such as communication tools, CRM systems, email platforms, and project management software, can significantly reduce employee focus and productivity. AI agents serve as an integration layer, retrieving information and executing actions across systems within a single interface.
- The Impact: Employees experience improved concentration and sustained workflow continuity, resulting in higher-quality output and reduced cognitive fatigue.
4. Scalability
- When workload spikes, such as during a holiday rush or a product launch, traditional teams struggle to keep up without hiring more staff. AI agents can scale instantly to handle increased volume, processing 10 invoices or 10,000 with equal ease.
- The Impact: The agility to grow and handle surges in demand without the slow, expensive process of recruiting and onboarding temporary staff.
5. Consistency and Compliance
- Humans can forget to update processes or skip steps when rushing. AI agents follow defined protocols every single time, ensuring strict adherence to compliance standards, brand guidelines, and security protocols.
- The Impact: drastically reduced risk of human error in sensitive areas like data entry, financial reporting, and legal compliance.
6. Enhanced Employee Satisfaction and Retention
- By automating repetitive and administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and routine tagging, AI agents reduce the burden of low-value work.
- The Impact: Employees are more engaged and motivated when they can focus on meaningful and intellectually stimulating responsibilities, leading to improved job satisfaction and higher retention rates.
7. Accelerated Time-to-Insight
- AI agents can rapidly analyze and synthesize large volumes of structured and unstructured data, including documents, internal communications, and market research, transforming raw information into actionable insights.
- The Impact: Decision-makers gain timely and accurate intelligence, enabling faster, more informed decisions without the need for manual data consolidation or lengthy reporting cycles.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adopting AI Agents For Employee Workflows
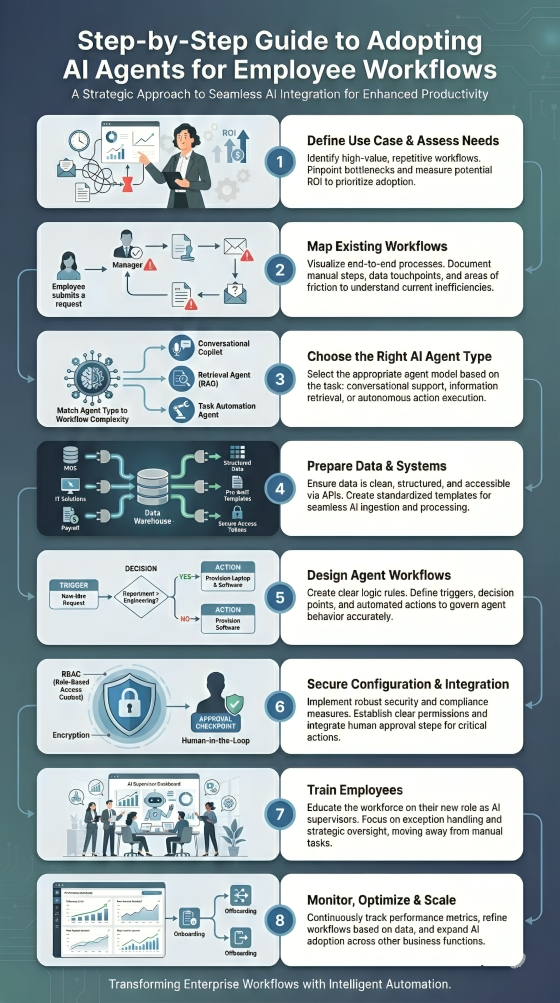
Step 1: Define Your Use Case and Assess Your Needs
Before selecting technology, the organization must clearly articulate the operational inefficiency it seeks to resolve. This involves identifying high-volume, repetitive processes that consume disproportionate human capital.
The Goal: To identify a specific bottleneck where an AI agent can deliver measurable return on investment (ROI).
Example Application (Onboarding):
The HR department identifies that onboarding a single employee requires 15 distinct manual emails and data entry across three different systems (HRIS, IT provisioning, and Payroll).
Manual latency delays the new hire's productivity by an average of 3 days. The objective is to reduce this administrative lead time to under four hours.
Step 2: Map Existing Workflows
One cannot automate what one does not understand. This step requires a granular audit of the current state, documenting every decision point, data transfer, and approval mechanism.
The Goal: To create a flowchart of the manual process to identify where the AI agent will intervene.
Example Application (Onboarding): The current workflow is mapped as follows:
- Candidate signs the offer letter.
- HR manually downloads the PDF and types details into the HR system.
- HR drafts an email to IT to request a laptop.
- HR drafts a separate email to the Hiring Manager to schedule orientation.
- Friction Point: If the IT request is missed, the employee starts without equipment.
Step 3: Choose the Right Type of AI Agent
Select the agent architecture that aligns with the complexity of the workflow. For example
- Conversational Assistants (Copilots): Best for drafting text and summarizing.
- Onboarding Example: Drafting a personalized welcome email for the new hire.
- Retrieval Agents (RAG): Best for searching internal databases to answer questions.
- Onboarding Example: Instantly retrieving the correct "Benefits Handbook" to attach to an email.
- Task-Specific Agents: Best for executing single, repetitive actions via API.
- Onboarding Example: Automatically creating a user profile in the payroll software.
Example Application (Onboarding):
Since this process requires reading a contract and executing tasks in external systems (sending emails, creating IT tickets), a simple chatbot is insufficient.
The organization selects an Autonomous Action Agent equipped with "tool-use" capabilities, allowing it to interface with both the HR software and the IT ticketing system via APIs.
Step 4: Prepare Your Data and Systems for Integration
AI agents require structured access to environments. This involves cleaning data repositories and ensuring the target software platforms have accessible Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
The Goal: To ensure the ecosystem is ready for machine-to-machine communication.
Example Application (Onboarding):
- Data Preparation: The HR team standardizes the "Offer Letter" templates so the AI can reliably parse fields like Start Date, Role, and Salary.
- System Prep: The IT team generates API keys for the ticketing system (e.g., Jira/ServiceNow) and grants the AI agent permission to "Create Ticket" but not "Delete Ticket."
Step 5: Design Agent Workflows
This phase involves programming the logic of the "triggers" that initiate the agent, as well as the "actions" it must perform in sequence. This typically involves defining "If-Then" logic combined with natural language understanding.
The Goal: To construct the operational architecture of the agent.
Example Application (Onboarding): The workflow is designed as follows:
- Trigger: A document labeled "Signed_Offer.pdf" is uploaded to the secure HR folder.
- Action 1: Extract "Name" and "Department."
- Action 2: Check "Department." IF Department = "Engineering," THEN request "MacBook Pro" in the IT system. IF Department = "Sales," THEN request "Windows Laptop."
- Action 3: Send a welcome email to the candidate with the orientation schedule.
Successfully deploying these specific architectures, particularly those involving RAG and LLM integrations, requires a solid grasp of the underlying technologies.
The Certificate Program in Generative and Agentic AI Fundamentals from Johns Hopkins University offers professionals a structured pathway to master these core concepts.
Certificate Program in Generative AI & Agents Fundamentals
A program focused on the foundational concepts of Generative AI and AI agents. It covers topics like NLP, Prompt Engineering, and Responsible AI, with practical applications for various industries.
The curriculum provides hands-on experience with Large Language Models, Prompt Engineering, and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), ensuring learners understand the technical foundations necessary to select and implement the right agentic solutions for their needs.
Step 6: Configure and Integrate the AI Agent Securely
Security is paramount. Organizations must implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure the agent only accesses necessary data and operates within strict boundaries (guardrails).
The Goal: To deploy the agent while mitigating data privacy risks and potential "hallucinations."
Example Application (Onboarding):
The IT Security team configures the agent with Least Privilege Access. The agent is permitted to read specific folders containing offer letters, but is blocked from accessing sensitive payroll history files.
Additionally, a "Human-in-the-Loop" gate is established: the agent prepares the IT equipment request, but an HR manager must click "Approve" before the order is finalized.
Step 7: Train Employees
Successful adoption depends on human acceptance. Employees must be trained not only on how to use the tool but on how their roles shift from "doers" to "supervisors" of the AI.
The Goal: To facilitate change management and ensure staff can effectively collaborate with the agent.
Example Application (Onboarding):
HR staff are trained on the new dashboard. Instead of manually typing data, they are taught how to review the agent's activity logs.
They are also instructed on protocol for handling exceptions, for instance, if a new hire has a dual role that the agent's logic cannot categorize, the employee knows how to intervene and override the agent manually.
Step 8: Monitor, Optimize, and Scale
Post-deployment, the system requires continuous observation. Performance metrics should be analyzed to identify errors or opportunities for expanded functionality.
The Goal: To validate the ROI and refine the agent's accuracy over time.
Example Application (Onboarding):
- Monitor: Review logs to ensure the agent correctly distinguished between "Engineering" and "Sales" equipment requests.
- Optimize: Initial data shows the agent struggles with international phone number formats. The team updates the prompt instructions to handle global dialing codes.
- Scale: Once the onboarding process is stable, the organization replicates this workflow model for "Employee Offboarding."
Common Challenges in AI Agent Implementation & Solutions
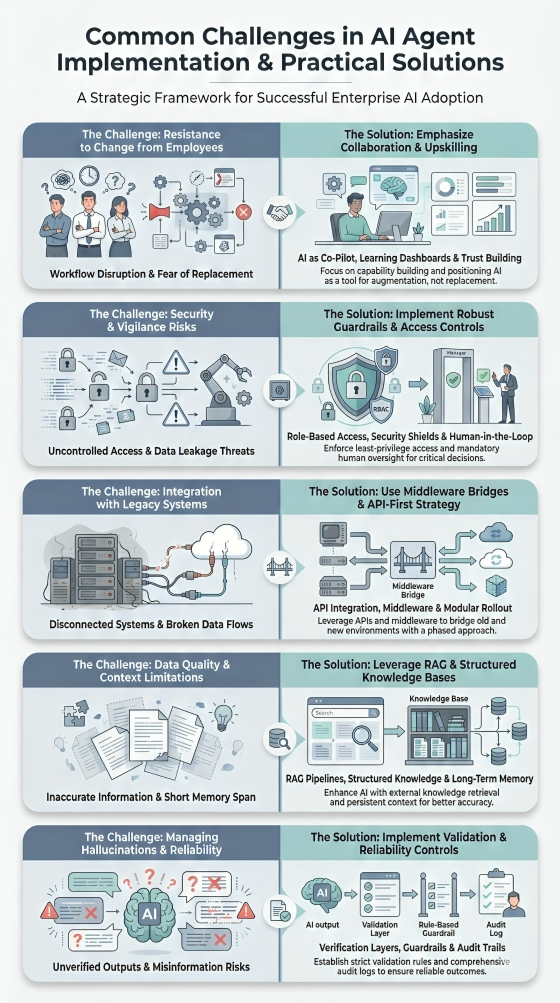
1. Resistance to Change from Employees
Employees may view AI agents as a threat to their job security or feel intimidated by new workflows, often leading to hesitation or low adoption rates.
How to Overcome
Position AI as a supportive "co-pilot" rather than a replacement by investing in comprehensive upskilling. Programs like PG Program in AI Agents for Business Applications from the University of Texas at Austin are designed to bridge this gap, helping professionals gain expertise in building and deploying autonomous agents.
PG Program in AI Agents for Business Applications
This program focuses on applying Agentic AI to solve business problems, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation. Learn to build AI agents using Generative AI, Large Language Models, and other advanced tools.
The curriculum covers Agentic Design Patterns, Multi-Agent Systems (using frameworks like CrewAI and AutoGen), and Strategic Implementation, empowering teams to lead AI initiatives and solve complex business problems confidently.
2. Security & Vigilance
Giving agents autonomy creates significant risks, such as data leakage, "prompt injection" attacks, or the agent executing unauthorized high-stakes actions (like deleting live data).
How to Overcome
Mitigate risks by enforcing strict "least privilege" access controls and sandboxing environments, while mandating human-in-the-loop approval for high-stakes actions to prevent unauthorized execution or data leakage.
3. Integration with Legacy Systems
AI agents often struggle to communicate with older, on-premise software or fragmented data silos that lack the modern APIs required for seamless interaction.
How to Overcome
Bridge the compatibility gap by building API middleware layers that translate legacy data for modern agents and adopting a modular rollout strategy, integrating with modern tools first before tackling complex, older ERPs.
4. Data Quality & Context Windows
Agents rely on data to make decisions; "garbage in, garbage out" leads to errors, while limited context windows can cause agents to "forget" instructions during long tasks.
How to Overcome
Enhance accuracy and retention by implementing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) linked to clean, audited knowledge bases, and utilizing long-term memory modules to prevent context loss during extended interactions.
5. Managing Hallucinations & Reliability
Unlike standard deterministic software, AI models are probabilistic. An agent might confidently provide a wrong answer or invent a nonexistent policy.
How to Overcome
Ensure reliability by implementing strict, hard-coded guardrails that the model cannot override and using secondary validation scripts to verify outputs, backed by detailed logs to trace and debug logic errors.
Conclusion
Integrating AI agents into employee workflows marks the definitive shift from managing tasks to driving innovation. By offloading routine complexities to intelligent agents, organizations don’t just save time; they reclaim their workforce's potential for high-impact strategy.