Goal: Create a Python Project that can download individual videos or an entire playlist from YouTube.
What you will learn in this tutorial:
- Importing and using external libraries: We will use a library called yt-dlp. It makes downloading videos and playlists from YouTube easy.
- Creating a user-friendly interface: Your program will ask the user what they want to download, and then guide them step-by-step.
- Applying if/else logic: If the user wants to download a video, download the video; else, the code for the playlist will run.
- Error Handling: If someone gives the wrong URL, the program will simply say “the URL is wrong” - and will not get confused.
- Breaking the code into parts (Functions): Your code will be a combination of small functions, so that it looks neat and it is easy to change later.
In this course, you will learn the fundamentals of Python: from basic syntax to mastering data structures, loops, and functions. You will also explore OOP concepts and objects to build robust programs.
Prerequisites
- Python: You must have Python 3 installed on your system. If not, install using this Python installation guide.
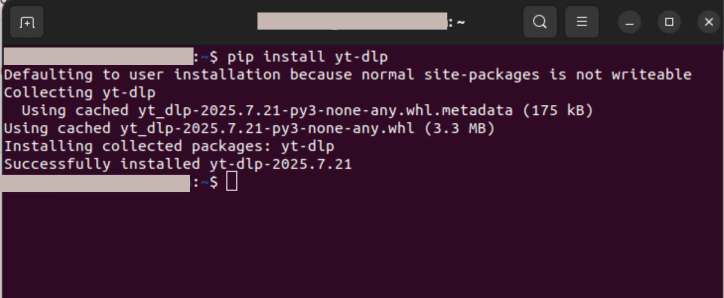
- yt-dlp library: This is the library we will be working with. To install it, open the terminal (or Command Prompt) and run this command:
pip install yt-dlp
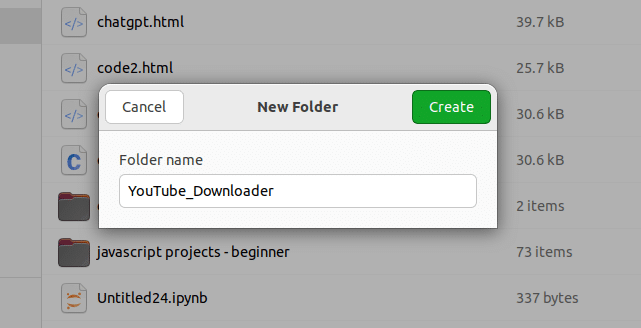
Step 1: Prepare your project folder
First, create a new folder for your project. Name it something like YouTube_Downloader.
Now, create a new file inside this folder, using your favorite code editor - be it VS Code, Sublime Text, or Notepad, and name it downloader.py.

Step 2: Writing Python code
This is where the real game begins.
We will write the code into different modules. We will start with a main function, which will guide the user on what to do next. Here is the complete code:
# Importing libraries to run command-line tools and manage files
import subprocess
import os
# --- Helper Functions ---
def download_video(url, output_path='Videos'):
"""
Function to download a single YouTube video using yt-dlp
"""
try:
print(f"Fetching video from {url}...")
# Ensure the output directory exists
os.makedirs(output_path, exist_ok=True)
# Construct the command to download the best quality video/audio and merge them
command = [
'yt-dlp',
'-o', os.path.join(output_path, '%(title)s.%(ext)s'), # Saves as 'Video Title.mp4' etc.
url
]
subprocess.run(command, check=True) # Run the command and check for errors
print(f"✅ Downloaded successfully!") # Downloading message
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
print("❌ Error: Failed to download. Check if the URL is correct and yt-dlp is working.")
except Exception as e: # Any other error
print(f"❌ An error occurred during download: {e}")
def download_playlist(url, output_path='Playlists'):
"""
Function to download all videos in a YouTube playlist using yt-dlp
"""
try:
print(f"Starting download for playlist: {url}")
# The output template '%(playlist)s/%(playlist_index)s - %(title)s.%(ext)s'
# tells yt-dlp to create a folder named after the playlist title.
output_template = os.path.join(output_path, '%(playlist)s/%(playlist_index)s - %(title)s.%(ext)s')
command = [
'yt-dlp',
'-o', output_template, # Set the output template
'--yes-playlist', # Confirm downloading a playlist
url
]
subprocess.run(command, check=True)
print("\n✅ Playlist download complete!")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
print("❌ Error: Failed to download playlist. Check the URL and your connection.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ An error occurred with the playlist URL: {e}")
# --- Main Program Logic ---
def main():
"""This is the main function which will ask the user what to download and run the correct function
"""
print("--- Welcome to the YouTube Downloader! ---")
while True:
# Ask the user if they want a video, playlist or exit the program
mode = input("\nDo you want to download a (1) single video or a (2) playlist? (Enter 1 or 2, or 'q' to quit): ")
if mode.lower() == 'q': # Exit if user enters 'q'
print("Goodbye! 👋")
break
elif mode == '1': # If downloading a video
video_url = input("Enter the YouTube video URL: ")
download_video(video_url)
elif mode == '2': # If downloading a playlist
playlist_url = input("Enter the YouTube playlist URL: ")
download_playlist(playlist_url)
else: # If wrong option selected
print("That's not a valid option. Please try again.")
# Entry point of the script (this is what runs when you run the file directly)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Add the above code to the file downloader.py.
Step 3: Run the script
- Open the terminal
- In Windows → Open Command Prompt or PowerShell
- In Mac and Linux → Open Terminal
- Go to your project folder
Use the cd command to navigate to the folder where your script is located.
In Windows:
cd C:\Users\YourName\Desktop\YouTube_Downloader
In Mac/Linux:
cd /home/YourName/Desktop/YouTube_Downloader
or
cd ~/Desktop/YouTube_Downloader
- Run the script
The command is the same for all three – Windows, Mac, Linux:
python downloader.py
If your system runs python3 instead of python, run this:
python3 downloader.py
The program will now ask you:
- Press '1' → to download a video, then paste the URL.
- Press '2' → to download the entire playlist, then paste its URL.

Where to find the downloads
Whatever you download will be saved in your project folder.
If you have downloaded playlists, a separate folder will be created for each playlist.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do I add a progress bar to a download?
yt-dlp does this automatically. When you run the script, a detailed progress bar will appear directly in the terminal - including the download speed, file size, and the time left. You don't need to write any extra code for this.
Q2: What if I want to change download options, like download only audio - how do I do that?
You can do this by adding extra flags to the yt-dlp command in the Python script.
Let’s say you only want the audio and save it as an MP3 file, then change the command list in the download_video function like this:
Inside the download_video function
command = [
'yt-dlp',
'-x', # to extract only the audio
'--audio-format', 'mp3', # to convert to mp3
'-o', os.path.join(output_path, '%(title)s.%(ext)s'),
url
]
yt-dlp has hundreds of options to change the format, quality, subtitles, and more.
Q3: Error in script, what to do now?
Usually, the problem occurs due to these reasons:
- Incorrect URL
- Internet not working
yt-dlpis not installed or not working
First check whether the URL you have entered is a direct link to the correct YouTube video or playlist.
If it still does not work, then it is possible that your yt-dlp library is out of date, because YouTube often changes its system. Update it by running:
pip install --upgrade yt-dlp
Q4: Why is there no sound in the downloaded video?
This problem is common with other methods, but yt-dlp fixes it automatically. In fact, when you watch a high-quality video, YouTube provides the video and audio in separate files. yt-dlp is smart enough to download the best version of both and then combine them into one high-quality file.
This is why it is important to install FFmpeg, because yt-dlp uses it to combine the video and audio. Once you have this setup, the no sound problem is gone.
Q5: Why did we choose yt-dlp?
There are other libraries, but we chose yt-dlp because it is very powerful, reliable, and always updated. It is the community's standard tool for downloading videos.
When we call it from Python, we get the benefits of both Python's simple interface and yt-dlp's powerful, up-to-date downloader that does all the heavy lifting. And yes, it even handles tricky things like audio-video integration automatically.
Also Check: