The India AI Impact Summit 2026, held at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, marked a significant moment in the global AI ecosystem.
Moving beyond theoretical discussions, the summit outlined a clear roadmap for embedding artificial intelligence into national infrastructure, governance, and workforce development.
With participation from over 20 Heads of State, 60 Ministers, and 500 global AI leaders, the event highlighted India’s shift from being a technology consumer to becoming a strategic architect of AI systems.
Centered on the Three Sutras that is People, Planet, and Progress, the summit emphasized the transition from purely commercial AI to practical, impact-driven applications.
Key outcomes pointed to three major focus areas: wider access to high-performance computing, the development of a strong techno-legal governance framework, and a massive institutional push toward workforce transformation.
Let us explore these themes in detail.
Capital Commitments and Infrastructure

A primary highlight of the summit was the sheer scale of capital infusion and infrastructure expansion aimed at making India a global hub for AI.
The event served as a platform for combined investment commitments that are not merely speculative but are tied to tangible infrastructure projects designed to lower entry barriers for startups and researchers. Key infrastructure and financial milestones include:
Strategic Capital Commitments
The summit catalyzed massive capital inflows, positioning AI as the "next big infrastructure" for the nation.
- National Funding: The Indian government reinforced its commitment with the ₹10,300 crore ($1.25 billion) IndiaAI Mission. This fund is allocated across five years to subsidize compute access, support deep-tech startups, and build indigenous foundation models.
- Global Corporate Investment: Significant private sector pledges were announced, including:
Google: Unveiled the $15 billion AI Hub in Vizag and the "America-India Connect" project, a strategic subsea fiber-optic route linking the US, India, and the Southern Hemisphere to ensure high-speed data flow.
Microsoft: Committed to a $50 billion investment by 2030 to expand AI infrastructure across the Global South, with India as a primary anchor following a prior $17.5 billion commitment.
Tata Sons: Outlined plans for $120 billion in large-scale investments spanning semiconductors, EV batteries, and AI-driven manufacturing.
- Venture Capital Momentum: Industry experts project that over $200 billion in total investment will flow into the Indian AI ecosystem over the next two years, targeting all five layers of the AI stack.
The Infrastructure To Compute & For Data
To achieve "sovereignty," India is aggressively scaling its physical and digital compute capabilities.
- GPU Expansion: Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw announced the addition of 20,000 GPUs within a week of the summit, augmenting the existing base of 38,000 units. The goal is to cross the 100,000 GPU mark by the end of 2026.
- Democratized Access: Under the IndiaAI Mission, these high-end GPUs are provided to startups and researchers at a subsidized rate of ₹65 per hour, roughly 72 cents, making high-performance computing accessible to small-scale innovators.
- Semiconductor Sovereignty: With ten projects already approved, India is moving toward local production of AI-focused chips through the Semiconductor Mission 2.0, ensuring hardware security for its data centers.
- State-Backed Funding: To bolster the domestic innovation ecosystem, the Indian government earmarked $1.1 billion (₹10,372 crore) for the IndiaAI Mission. This fund supports the development of 12 indigenous foundation models and over 30 sector-specific applications in healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
To understand the fundamental shift from traditional assistants to the autonomous systems discussed at Bharat Mandapam, explore our deep dive on AI Agents and Agentic AI: A Look at What’s Ahead.
As these massive capital commitments drive the adoption of autonomous systems, the demand for professionals who can lead the shift from simple automation to goal-driven autonomy is reaching a fever pitch.
To prepare for this era of high-stakes investment, the Certificate Program in Agentic AI from Johns Hopkins University provides the technical and strategic depth required to architect systems that reason, plan, and pursue objectives independently.
Certificate Program in Agentic AI
Learn the architecture of intelligent agentic systems. Build agents that perceive, plan, learn, and act using Python-based projects and cutting-edge agentic architectures.
This 16-week online program equips professionals to solve complex business problems using Agentic AI. The curriculum builds strong foundations, covering ReAct, Chain-of-Thought (CoT), advanced agent architectures such as symbolic and BDI models, and tools including LangChain, LangGraph, AutoGen, CrewAI, and vector databases.
Learners also gain practical experience in Multi-Agent Systems, game theory-based coordination, and Reinforcement Learning for adaptive agents, helping them design, deploy, and manage intelligent autonomous systems in real-world enterprise environments.
Governance and Ethics: The "MANAV" Vision
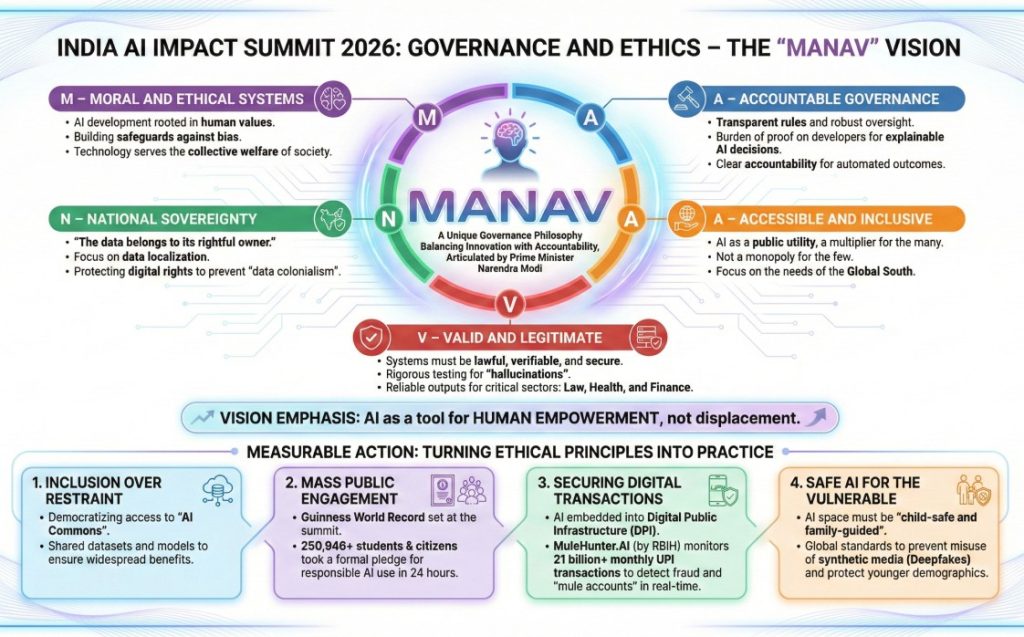
The summit introduced a unique governance philosophy that balances innovation with accountability. Prime Minister Narendra Modi articulated the "MANAV" Vision, an acronym standing for:
- M – Moral and Ethical Systems: AI development must be rooted in human values. This includes building safeguards against bias and ensuring that technology serves the collective welfare of society.
- A – Accountable Governance: This pillar calls for transparent rules and robust oversight. It shifts the burden of proof to developers to ensure that AI decisions are explainable and that there is clear accountability for automated outcomes.
- N – National Sovereignty: A cornerstone of the Indian approach, this principle asserts that "the data belongs to its rightful owner." It focuses on data localization and protecting the digital rights of citizens to prevent "data colonialism."
- A – Accessible and Inclusive: India views AI as a public utility. The goal is to ensure that AI acts as a multiplier for the many, rather than a monopoly for the few, specifically focusing on the needs of the Global South.
- V – Valid and Legitimate: Systems must be lawful, verifiable, and secure. This involves rigorous testing for "hallucinations" and ensuring that AI outputs are reliable for critical sectors like law, health, and finance.
Unlike more restrictive regulatory models, this vision emphasizes that AI must remain a tool for human empowerment rather than a source of displacement.
The summit highlighted how these ethical principles are being converted into measurable action:
- Inclusion over Restraint: The focus is on democratizing access to "AI Commons" shared datasets and models, ensuring that the benefits of AI are not concentrated in the hands of a few entities.
- Mass Public Engagement: In a demonstration of grassroots ethical commitment, India set a Guinness World Record at the summit. Over 250,946 students and citizens took a formal pledge for the responsible use of AI within a single 24-hour window.
- Securing Digital Transactions: To ensure Accountable Governance in finance, AI is being embedded into the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). Systems like MuleHunter.AI, developed by the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH), now monitor over 21 billion monthly UPI transactions to detect fraud and identify "mule accounts" in real-time.
- Safe AI for the Vulnerable: The PM stressed that the AI space must be "child-safe and family-guided," calling for global standards to prevent the misuse of synthetic media (Deepfakes) and protect younger demographics from harmful algorithms.
Career Transformation: Preparing the AI-Ready Workforce
The summit decisively shifted the workforce conversation from "job displacement" to "career augmentation," focusing on the concept of Human Capital as India’s primary competitive advantage.
With AI talent in India projected to grow to over 12.5 lakh professionals by 2027, the event outlined an aggressive institutional framework to prepare citizens for an AI-integrated economy.
Institutional Skilling Frameworks
The government and industry partners introduced a tiered approach to ensure that every segment of the workforce is AI-ready:
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: This flagship initiative is designed to build a high-end research and development pipeline by supporting 500 PhD scholars, 5,000 postgraduates, and 8,000 undergraduates. The goal is to move beyond simple coding to deep-tech innovation in areas like computer vision and natural language processing.
- Mass Public Sector Reskilling: In one of the world's largest digital literacy drives, a partnership with Karmayogi Bharat aims to train 20 million public servants across 800+ districts. This ensures that the administrators of the nation can effectively leverage AI tools in governance and service delivery.
- Grassroots "Nano-Credentials": The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) announced the SOAR (Skilling for AI Readiness) program. This involves short-duration, industry-aligned certifications for blue-collar and informal workers, enabling them to use AI-driven tools in sectors like agriculture, construction, and textile design.
As India aims for 12.5 lakh AI professionals by 2027, stay ahead by mastering the Essential AI Skills for Career Success in 2026.
Market Dynamics and Economic Projections
The summit provided data-driven insights into how AI is expected to reshape the broader economy:
- IT Sector Evolution: Contrary to fears of obsolescence, AI is expected to propel India's IT sector to a $400 billion industry by 2030. The shift will be driven by AI-enabled outsourcing and domain-specific automation.
- Startup Ecosystem: Out of India's 1.8 lakh startups, nearly 89% of new launches last year integrated AI into their products, signaling that "AI-first" is the new default for entrepreneurship.
- New Job Sectors: Emerging fields such as Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, and Comics (AVGC) are projected to generate nearly 2 million new jobs by 2030, supported by AI-aligned Content Creator Labs in 15,000 schools.
With of new startups integrating AI, discover where you fit in the new ecosystem with our guide to 8 High-Demand AI Jobs in 2026.
As the job market shifts toward specialized skills, the value of structured, accredited learning becomes paramount.
The summit highlighted, the transition from job displacement to career augmentation requires a workforce capable of navigating the "sovereign stack." To meet this demand for specialized talent, the Certificate in Generative AI from IIT Bombay offers a direct pathway for professionals to master the very LLM-first architectures discussed at Bharat Mandapam.
This five-month online program covers foundations such as Python, Deep Learning, and NLP, and advances into Transformers, RAG, fine-tuning, and LLM workflows.
As the summit highlighted the need for secure and governed AI systems, this program directly addresses these requirements through its module on LLMOps and Governance, covering CI/CD for LLM applications, live performance monitoring, and mitigating vulnerabilities.
After completion, the graduates emerge with the ability to build agentic applications that plan tasks and coordinate multi-step workflows, supported by a toolkit that includes PyTorch, TensorFlow, LangChain, and LangGraph.
Launch of India’s AI Innovations In Summit
Launch of India’s AI Innovations In Summit
Beyond the high-level policy discussions, the event showcased three landmark indigenous innovations, Sarvam AI (Vikram), SATHEE, and PARAM, that together define the new "Sovereign AI" paradigm.
1. Sarvam AI: India’s First Sovereign Large Language Model (Vikram Series)
Bengaluru-based Sarvam AI unveiled the Vikram series, a suite of Large Language Models (LLMs) built specifically for the Indian context. Developed using the IndiaAI Mission's compute infrastructure and 4,096 NVIDIA H100 GPUs, this series addresses the "token inequality" often faced by Indian languages in Western models.
- Capabilities: The series includes Vikram-105B (105 billion parameters) for complex enterprise reasoning and Vikram-30B (30 billion parameters) for real-time conversational agents. These models were trained on over 16 trillion tokens, encompassing high-quality data across all 22 official Indian languages.
Key Advantages:
- Linguistic Precision: Unlike global models, Vikram understands regional dialects and code-switching (e.g., "Hinglish"), providing 84.3% accuracy on India-specific document intelligence tasks.
- Resource Efficiency: Utilizing a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, the 105B model activates only 9 billion parameters per token, making it significantly more energy-efficient and cost-effective than dense global alternatives.
- Strategic Autonomy: By hosting data and training within India, Sarvam ensures that sensitive citizen information remains under national jurisdiction, fulfilling the MANAV principle of National Sovereignty.
2. SATHEE: The AI-Driven Democratization of Education
Developed by IIT Kanpur and the Ministry of Education, the SATHEE (Self-Assessment, Test and Help for Entrance Exams) platform was unveiled as the world’s largest AI-powered open learning initiative.
- Capabilities: The 2026 version integrates an AI Conversational Tutor and a Visual Problem Solver. It currently supports preparation for major national exams, including JEE, NEET, CUET, and CLAT, and attracted over 4,700 submissions for its global challenges.
Key Advantages:
- Universal Equity: The platform is completely free of cost, offering "Tier-1" coaching quality to students in rural and underserved districts who cannot afford private tutorials.
- Adaptive Pedagogy: Using Adaptive Learning Paths, the AI detects individual learning gaps and tailors study plans in real-time, providing personalized mentorship at a population scale.
- Linguistic Inclusion: Resources are available in multiple Indian languages, ensuring that a student’s potential is not limited by their proficiency in English.
3. PARAM: The Indigenous Robotic Quadruped
While software dominated the pavilions, PARAM, built by the Bengaluru startup General Autonomy, proved India’s growing prowess in advanced robotics.
- Capabilities: PARAM is a 35kg quadruped (robot dog) engineered for rugged Indian terrains. It features autonomous navigation, target tracking, and the ability to climb stairs up to 30cm high.
Key Advantages:
- Industrial Resilience: With a top speed of 3m/s and a battery life of 8 hours (with hot-swappable batteries), it is designed for hazardous industrial inspections, factory automation, and disaster response.
- Sovereign Hardware: Unlike assembled imports, PARAM is custom-built with local actuators and edge-AI integration. This ensures that the robot can operate without a constant cloud connection, which is vital for secure defense and infrastructure monitoring.
- Mechanical Agility: It can perform "crab walks" for low-height entries and features automatic fall recovery, making it significantly more versatile than traditional wheeled robotic systems.
By building foundational models, scalable education platforms, and indigenous robotics solutions, India is strengthening its technological sovereignty while ensuring that AI serves national priorities. This marks not just progress in innovation, but the foundation of a self-reliant and globally competitive AI ecosystem.
Conclusion
The India AI Impact Summit 2026 has successfully reframed the AI narrative from one of "existential risk" to one of "developmental opportunity." By committing substantial capital, expanding computing infrastructure, and prioritizing a human-centric governance model, India has established a blueprint for other emerging economies to follow.
For the professional community, the message is clear: the integration of AI is no longer an optional digital upgrade but a foundational shift in how industries operate. The focus has moved toward creating "sovereign AI" systems built on local data, for local challenges, governed by local values.
As the nation moves toward a projected USD 1.7 trillion AI-driven economic contribution by 2035, the premium on specialized knowledge and adaptive skills will only continue to rise. Navigating this future will require a commitment to lifelong learning and a strategic understanding of the policy shifts that now define the global technology era.









