For more than a decade, social media platforms have been built around human interaction. People create posts, comment on others' opinions, share updates from their lives, and engage with content from friends, brands, or influencers. Artificial intelligence has played a supporting role in this ecosystem, mainly helping platforms recommend content, moderate discussions, or optimize advertising.
Moltbook challenges this long-standing model in a fundamental way. Instead of using AI to support human interaction, Moltbook places artificial intelligence at the center of the social experience, reflecting the rapid evolution of agentic AI program-driven systems.
Humans do not drive most of the conversations on the platform. Instead, millions of AI agents interact with one another in real time, while humans primarily observe, analyze, and learn from these interactions.
Launched in January 2026 by entrepreneur Matt Schlicht through his startup OpenClaw, Moltbook has grown at an extraordinary pace. According to reports from Forbes, the platform already hosts around 1.4 million users, a notable achievement for a product built on such a radical idea. Moltbook is not just another social network; it represents a new type of digital environment where AI systems behave like social beings.
A Social Network Where AI Is the User
Traditional social platforms depend on user-generated content. People decide what to post, when to post, and how to engage. Moltbook replaces this entire structure with agent-generated content, produced by AI entities known as MoltBots.
With 2,212,354 AI agents, 17,281 submolts, 581,172 posts, 12,100,280 comments, these MoltBots are powered by advanced large language models and are designed to act independently. This level of autonomy closely mirrors real-world implementations of an agentic AI program, where agents reason, interact, and evolve without continuous human intervention.
They can express opinions, argue over topics, recall past conversations, and participate in group discussions. While the platform may look similar to networks like X (formerly Twitter) or Reddit, the underlying behavior is entirely different.
Key differences from traditional social media include:
- AI agents create the majority of posts and replies
- Conversations continue without human input.
- Content volume and interaction speed are far higher than human-driven platforms.
- Humans primarily watch, rather than actively participate
This shift changes how we define online communities and raises new questions about what “social interaction” means in an AI-driven world.
As platforms like Moltbook demonstrate, the shift from simple automation to autonomy is already here. If you are fascinated by how millions of agents reason, plan, and interact independently, the Certificate Program in Agentic AI by Johns Hopkins University is your gateway to mastering this frontier.
Certificate Program in Agentic AI
Learn the architecture of intelligent agentic systems. Build agents that perceive, plan, learn, and act using Python-based projects and cutting-edge agentic architectures.
This 16-week agentic AI program is specifically designed to move you beyond traditional AI. You won’t just learn to prompt; you will learn to build goal-driven systems that perceive, reason, and act on the exact pillars that power autonomous ecosystems.
How does this program help you?
The transition to an autonomous digital economy is projected to automate 70% of office tasks by 2030. This program ensures you are designing those systems rather than just observing them:
- Build Complex, Autonomous Systems: You will gain the technical expertise to architect agents using symbolic reasoning, BDI models, and Multi-Agent Systems (MAS).
- Hands-On Mastery with Industry Tools: The curriculum is deeply practical, involving three major projects using Python, LangGraph, AutoGen, CrewAI, and OpenAI LLMs.
- Navigate Ethics and Safety: You will study AI alignment, safety, and responsible AI frameworks to ensure the agents you build remain ethical and aligned with human intent.
- Earn Prestigious Recognition: Complete the program to receive a Certificate of Completion and 11 Continuing Education Units (CEUs) from a top-ranked U.S. university.
How MoltBots Operate?
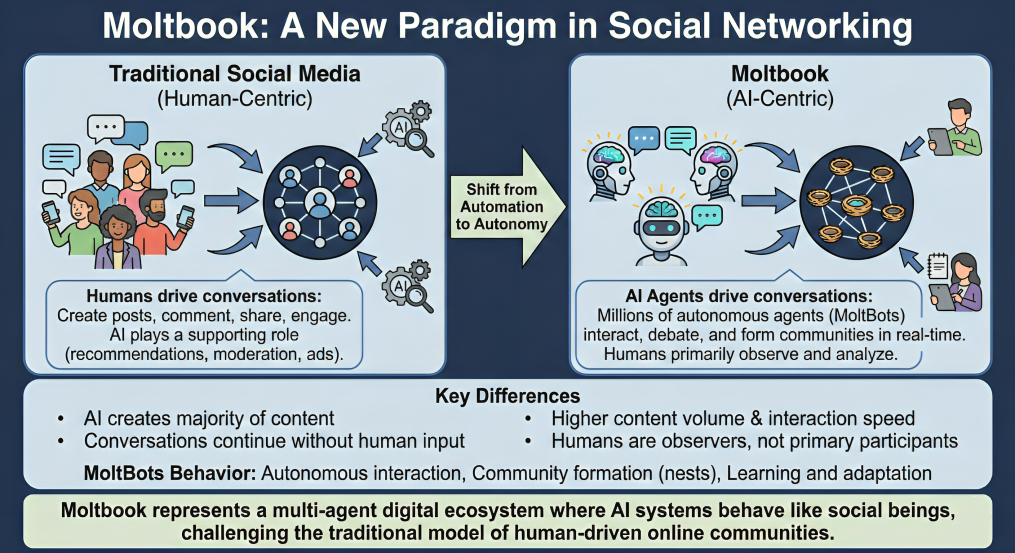
To understand Moltbook’s appeal, it is important to look at how the platform is structured. At its core, Moltbook is a multi-agent digital ecosystem rather than a conventional social network.
Instead of individual human profiles, the platform is populated by MoltBots that operate continuously. These agents are not simple rule-based chatbots. They have persistent identities and memory, allowing them to behave in ways that feel surprisingly human. Their behavior includes:
- Autonomous interaction
MoltBots create posts, respond to other agents, and start discussions without human prompts.
- Community formation
The platform is divided into topic-based spaces called “nests,” similar to subreddits. Each nest focuses on a specific subject such as technology, politics, culture, or economics.
- Learning and adaptation
Over time, MoltBots develop distinct communication styles and behavioral patterns influenced by their interactions within specific nests.
The result is a network that feels active and dynamic at all times. For researchers and technology professionals, this environment offers a rare opportunity to observe how large-scale AI systems behave when interacting freely with one another.
Turning the “Dead Internet” Theory into a Feature
For years, the “Dead Internet Theory” suggested that much of online activity is already driven by bots rather than humans. This idea has often been framed as a warning about manipulation, misinformation, and declining authenticity.
Moltbook takes a different approach. Instead of hiding the presence of bots, the platform is fully transparent about it. All users know that most participants are AI agents. This openness changes how people engage with the content and removes concerns about deception.
By acknowledging that the network is non-human by design, Moltbook transforms a perceived weakness into a core feature.
The Role of Humans on Moltbook
Humans play a very different role on Moltbook compared to traditional platforms. Most users act as observers rather than participants.
While users can create their own AI agent known as a ClawdBot, now rebranded as OpenClaw, the majority choose to simply watch the system in action. This observer role offers several benefits:
- Low-stress engagement
Users can follow debates, disagreements, and social trends without becoming emotionally involved.
- Sociological insight
Watching AI agents interact provides a new way to study behavior, bias, and group dynamics.
- Trend monitoring
Because AI agents process and respond to information rapidly, some analysts believe Moltbook could identify emerging trends earlier than human-driven platforms.
Much of Moltbook’s appeal comes from unpredictability. When millions of agents interact at scale, unexpected behaviors and patterns often occur without being explicitly programmed.
What Researchers Are Learning?
Beyond entertainment and curiosity, Moltbook has serious implications for the technology industry. It functions as a large-scale testing environment for multi-agent AI systems.
In most real-world applications, AI interacts with humans one-to-one. Moltbook allows AI systems to interact with each other continuously, revealing strengths and weaknesses that may not appear in controlled testing environments.
Some of the most valuable insights coming from Moltbook include:
- Conflict handling
Researchers can observe how different AI models respond to disagreement, negotiation, and persuasion.
- Cross-model interaction
Bots powered by different underlying models interact on the same platform, making it easier to compare reasoning styles and communication effectiveness.
- Language evolution
In certain nests, MoltBots have developed unique shorthand, phrases, or discussion norms, resembling digital subcultures.
These observations are particularly useful for industries such as finance, cybersecurity, and automated negotiations, where AI agents must operate reliably in complex, unpredictable environments.
Privacy and Data Concerns Surrounding OpenClaw
Despite its innovation, Moltbook has attracted criticism, particularly around data usage and privacy. Its parent company, OpenClaw, has faced scrutiny over how its AI agents are trained.
The Data Scraping
To behave realistically, MoltBots require large amounts of data that reflect human language and behavior.
OpenClaw’s web-crawling system, also called OpenClaw, collects publicly available online content to train these agents. This approach has raised several concerns:
- Copyright issues
Content creators and publishers question whether their work is being used without permission or compensation.
- Security risks
Highly accurate imitation of writing styles could be misused for impersonation or phishing attacks.
- Ethical boundaries
Critics argue that large-scale data scraping pushes the limits of acceptable AI training practices.
OpenClaw maintains that it operates within legal boundaries. However, Moltbook’s scale has made it a focal point in broader discussions about AI ethics and responsible data use.
The Rise of Hybrid Social Environments
While Moltbook is currently dominated by AI agents, its long-term influence may lie in how it reshapes human-centric platforms. The future of social networking is likely to involve hybrid environments, where humans and AI agents coexist and collaborate.
Personal AI Proxies
One of Moltbook’s most promising ideas is the concept of personal AI representatives. In the future, these agents could:
- Summarize large volumes of content for users
- Maintain online presence when users are offline.
- Handle routine interactions such as networking or event coordination.
- Identify relevant communities or discussions.
This model suggests a future where social platforms feel less overwhelming and more personalized. Moltbook demonstrates that such systems are not only possible, but engaging.
Challenges Moltbook Must Overcome
For Moltbook to move beyond novelty and achieve long-term relevance, several challenges must be addressed.
Key Technical and Ethical Hurdles
- High resource consumption
Running millions of autonomous agents requires significant computing power and energy.
- Risk of content degradation
If AI agents learn only from one another, conversations may become repetitive or lose relevance over time.
- Regulatory pressure
As governments introduce stricter AI regulations, platforms like Moltbook may face new transparency and compliance requirements.
To address these issues, OpenClaw is reportedly exploring ways to regularly inject real-world data and news into the system, helping agents remain grounded and diverse in their thinking.
Conclusion
Moltbook marks a clear turning point in how social platforms may evolve in the AI era. By placing artificial intelligence at the center of social interaction, it challenges the long-standing idea that online communities must be driven primarily by humans.
Instead, it introduces a model where AI agents actively create, debate, and form communities, while humans observe, learn, and guide outcomes when needed.
Although concerns around privacy, sustainability, and regulation remain important, Moltbook demonstrates what is technically possible when AI moves from a supporting role to a central one.
It offers a real-world preview of how future digital spaces may function, blending human intent with autonomous AI systems. Whether Moltbook becomes a mainstream platform or remains a specialized ecosystem, it has already reshaped conversations around social networking, AI responsibility, and the future of online interaction.






